What is Voip?
A Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phone system allows users to make voice calls using the internet, rather than a phone line. This results in a far less expensive and far more flexible communication method, enabling a variety of user-friendly features to be introduced alongside the basic call functionality.

Why Switch From ISDN To VoIP?
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a phone system that utilises the public switched telephone network (PSTN). ISDN lines are hardwired, whereas VoIP simply relies on the user having an internet connection. Some of the benefits of making the switch to VoIP are:
– ISDN lines will become redundant over the next few years
– VoIP is a far more feature rich environment
– Significantly lower call costs
– Flexibility; making office moves and expansion easy
– VoIP can be operated over a variety of platforms
How Does a VoIP Phone System Work?
Codecs are compression technologies and have two components, an encoder to compress the files, and a decoder to decompress.
VoIP works by converting your analogue voice signals into digital signals which are then transferred as data across your broadband line to the other person on the call
So, when you make a call, your voice signals are compressed, sent via an IP and then decompressed almost instantaneously.
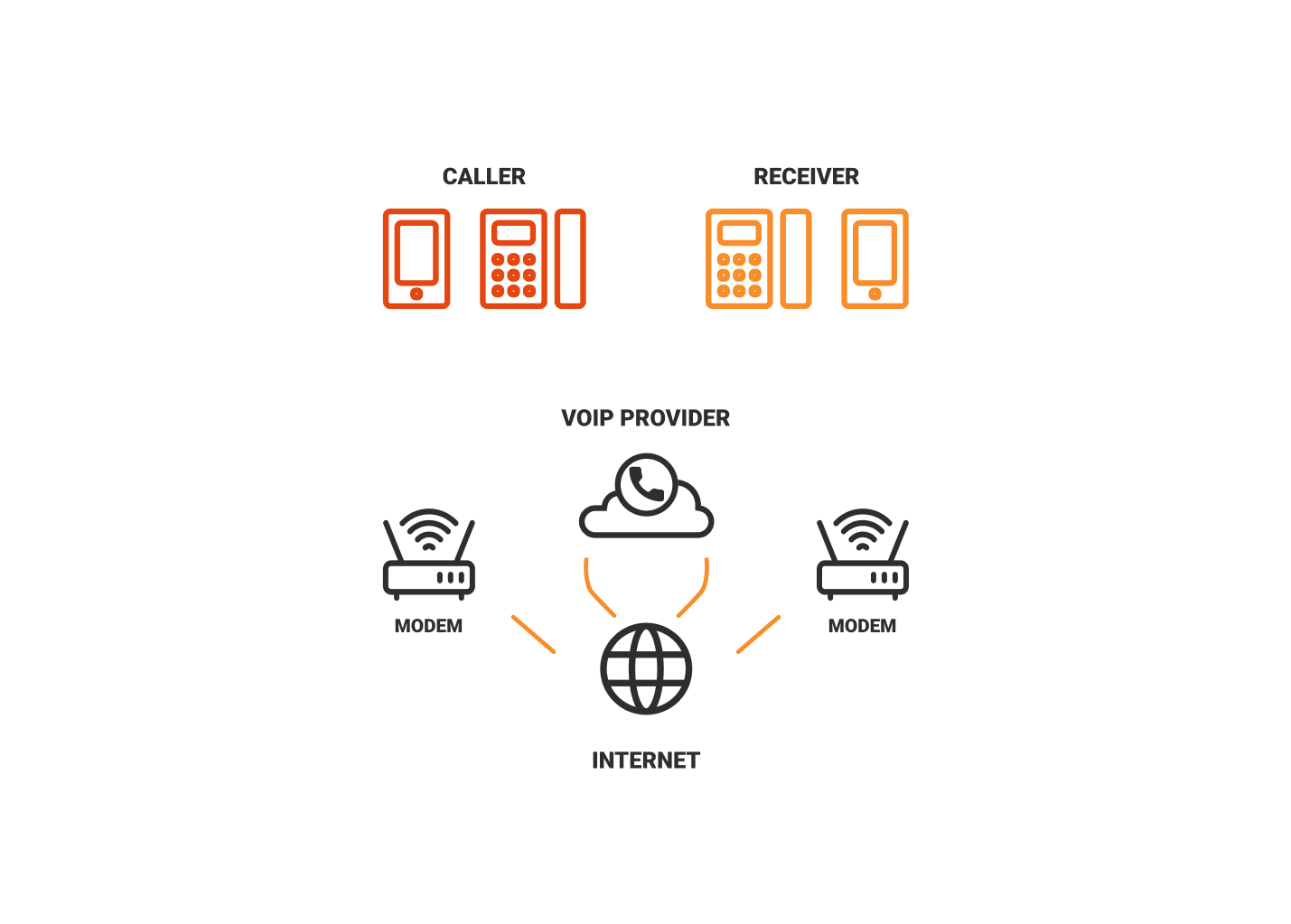
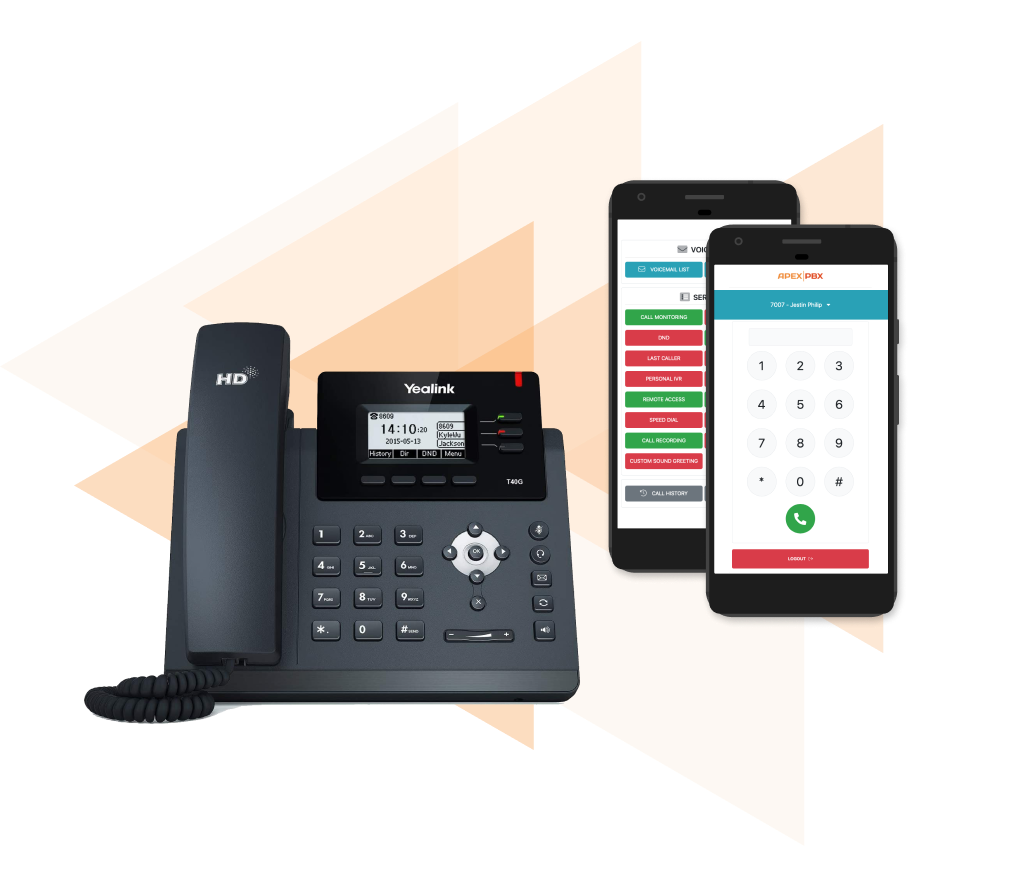
VoIP Hardware Or Software (App)?
Which solution is for you?
If you’re predominantly office-based during working hours, having hardware separate to your computer or personal mobile phone might be a preference. As flexibility around working hours and remote working grows, having the ability to handle incoming and outgoing calls while on the go may be more of a priority. This is where a softphone really comes in handy.
Variety is the spice of life, and there’s no reason why you can’t use your physical handset in conjunction with a softphone.

Advantages Of VoIP
VoIP And Disaster Recovery
Whether or not a company allows employees to work from home on a regular basis, VoIP can be hugely beneficial in unprecedented situations when a business has to temporarily close its headquarters. In the case of power cuts, internet failure, acts of God or illness, VoIP makes relocating staff a far easier process. Call forwarding to mobiles, as well as soft phones ensures there is no impact to a company’s ability to communicate with its clients or internally, even in the most exceptional of situations.

VoIP Key Features
Terminologies
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)
The set of rules that makes it possible to use the Internet for telephone or videophone communication
PBX (Private Branch Exchange)
A private telephone network used within a business
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network)
A set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the traditional circuits of the PSTN
PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network)
The aggregate of the world’s circuit-switched telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators
Cloud-Based
Data stored, managed, and processed on a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet, rather than on local servers or personal computers
Bandwidth
The maximum rate of data transfer across a given path
Latency
The delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer
IP (Internet Protocol)
A digital media transport system that runs over standard IP networks
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
The way a computer connects to the Internet at high speeds using telephone lines
Codecs
A device or program that compresses data to enable faster transmission and decompresses received data
IVR (Interactive Voice Response)
A technology that allows a computer to interact with humans through the use of voice and DTMF tones input via a keypad
RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
A network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks
SIP Trunking
Enables the end point’s PBX to send and receive calls via the Internet
Softphone
A piece of software that allows the user to make telephone calls over the Internet
FAQs
What happens if the internet goes down?
Your main telephone number can be forwarded instantly to a mobile number of your choice. For making outbound calls, the mobile application enables you to make calls as if you were working from your physical handset, displaying either your DDI or main number when dialling out.
Can I retain my existing number?
Yes. When porting numbers, the process normally takes anything between 2-4 weeks. When assigning new numbers, the system can be set up within 3-5 working days based on you having the correct infrastructure in place (internet/cabling/network services etc).
Can I use my existing broadband?
Yes, you can. We can also supply you with ADSL & Fibre broadband.
How long does it take to set up?
Overall the process takes between 2-4 weeks. This is dependent on ported (existing) numbers being accepted and engineer availability.
How do I add new extensions?
You can do this by informing your account manager that you want to add new handsets. Handset can usually be added in a matter of (ADAM TO SUPPLY TIMELINE)